WHAT IS THE ENTERPRISE DATA LIFECYCLE?
The Enterprise Data Lifecycle (EDLC) refers to the eight stages that data goes through from its creation to its eventual disposal as seen from the strategic enterprise perspective. The goal of the data lifecycle is to ensure that data is managed in a secure, efficient, and cost-effective manner throughout its entire existence while still providing operational value as a production asset, reference, back-up, or archive. At Peregrine, we view the EDLC as a frameworked process that outlines the natural progression of data over its lifetime. This enables organizations to create data management structures that correspond to the various stages of the EDLC process while driving enterprise-wide data cultures that support data-driven decisions.
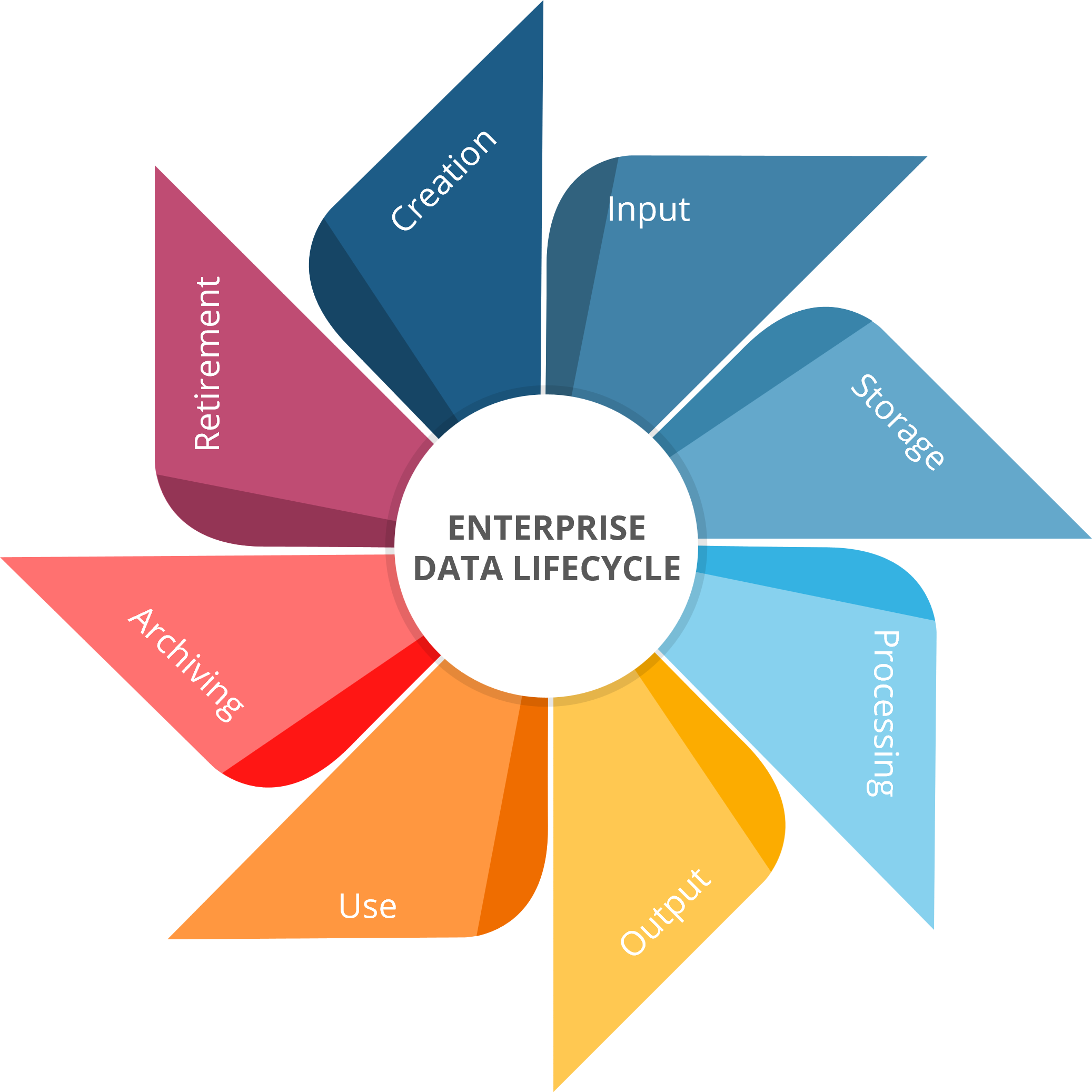
We break the EDLC into the following stages:
Data Creation: This stage involves the creation of new data, typically through data entry or data collection processes. The data creation stage is the starting point of the data lifecycle.
Data Input: This stage involves the entry of data into the organization's systems, such as databases or data warehouses. Data input can be done manually or through automated processes.
Data Storage: This stage involves the storage of data in the organization's systems. The goal of this stage is to ensure that data is stored in a secure, efficient, and cost-effective manner.
Data Processing: This stage involves the processing of data, such as data analysis, data integration, or data transformation. The goal of this stage is to make data more useful and usable for the organization.
Data Output: This stage involves the extraction of data from the organization's systems, typically for use in decision-making or reporting. Data output can be in the form of reports, visualizations, or other forms of data presentation.
Data Use: This stage involves implementing the data outputs in production-level systems or utilizing them to drive business value through data-driven decision-making. The objective of this stage is to drive core operational or business value using data outputs.
Data Archiving: This stage involves the long-term storage of data that is no longer needed for its original purpose, but may still be needed for legal, regulatory, or business reasons. The goal of this stage is to ensure that data is retained in a secure and accessible manner.
Data Retirement: This stage involves the safe disposal of data that is no longer needed for any purpose. The goal of this stage is to ensure that data is disposed of in a secure and responsible manner, in accordance with the organization's data retention policies and procedures.
It is important to note that the EDLC is an important aspect of overall data management, as it helps organizations to conceptualize the steps data will pass through and ensure that data is managed in a secure, efficient, and cost-effective manner in all stages of its lifecycle. Effective data management practices will include implementing data governance policies that address organizational needs around access and use of data; systems to ensure data quality; and policies and technical systems to ensure that data is secure within each stage and as it transits between stages. Our goal is to assist large and complex organizations to develop and follow a well-defined EDLC that is specifically tailored to their mission, vision, goals, and resources, so that they can improve the quality of their data, enhance data security, and ensure that data consistently and appropriately to drive business value through production systems and data-driven decision making.